HACCP- Hazard Analysis & Critical Control Point
My
current blog is a must read for all those who are associated with Food
production, kitchen and also for those who work in kitchen.
As each
sector is experiencing heavy growth and development, Kitchen is not an
exception either. The fundamentals of kitchen have excelled and the quality of
kitchen has been enhanced as well.
The
detail regarding this topic can be read more appropriately in Principles of Food Production Operations.
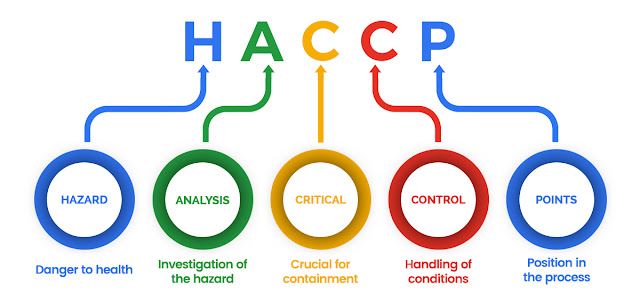
Hazard
Analysis & Critical Control Point is a system adopted by Codex Alimentarius
Commission. It is
conceptualized with a set of principles that actually is the framework of this
systematic system, based on science. It identifies specific hazards, evaluates
and provides measures for their control to ensure the safety of the food. Thus
actually it is a tool that assesses hazards and thereby establishes control
systems. It has mushroomed to such a level, that it has become the need of the
hour in food sector operations.
HACCP is
concerned right from the purchase of the food material till the final
consumption of the food material. Associated with multiple benefits, it has
strengthen the assurance regarding the quality of food safety management
system, and also aided to reduce the food cost by controlling the wastage due
to microbial infestation
The
HACCP system is based on seven principles mentioned below:
Principle 1: Conduct a hazard analysis.
Principle 2: Determine the Critical Control Points (CCPs).
Principle 3: Establish critical limits.
Principle 4: Establish a system to monitor control of the
CCP.
Principle 5: Establish the corrective action to be taken
when monitoring indicates that a particular CCP is not under control.
Principle 6: Establish procedures for verification to
confirm that the HACCP system is working effectively.
Principle 7: Establish documentation concerning all
procedures and records appropriate to these principles and their application.
General Guidelines
Few
general guidelines associated with HACCP under certain actions are as such:
·
Cleaning and sanitizing food contact surfaces
Ø
The
food contact surfaces such as sinks, tables, equipments, thermometers, and
utensils must be washed before each use, between uses when dealing with
different types of raw ingredients like fish, meat, poultry or vegetable etc.;
and between uses when dealing with or preparing ready-to-eat foods and raw
animal foods; and whenever the contamination occurs or is suspected.
Ø
All
food contact surfaces must be washed with detergent solution, rinsed with clean
water and sanitized with sanitizing solution and then after allowed to dry
properly.
Ø
When
using 3-compartment sink units, first sink is used for washing with detergent
solution at or above 43oC, second sink for rinsing with clean water
and third sink for sanitizing with a sanitizing solution in hot water at or
above 77oC for about 30 seconds.
·
Controlling time temperature
during preparation
Ø
The
ingredients to be used in cold foods (sandwiches, or salads, etc.) should be
pre-chilled to the temperature at around 5oC or below.
Ø
The
food should be prepared closet to the serving time of the food.
Ø
When
the potentially hazardous food is not to be served immediately after cooking,
it should be quickly chilled.
Ø
The
cooked food should never be left at room temperature for more than 30 minutes
or around, but it should be refrigerated.
·
Cooking potentially Hazardous
Foods
Ø
If
a combination of meat product is to be used in a recipe, then cook the food to
the highest required temperature.
Ø
The
following temperature is the desired temperature for cooking:
§
63oC
for 15 seconds for seafood, beef, pork or eggs
§
69oC
for 15 seconds for grinded (beef, pork or fish) products, fish nuggets or
sticks, cubed steaks
§
74oC
for 15 seconds for poultry, stuffed fish, pork, beef or stuffed pasta
§
58oC
for 15 seconds for fresh, frozen, or canned fruits or vegetables. It can either
be held on steam table or kept in a hot box.
·
Personal Hygiene
Ø
One
has to be in good health, properly dressed in uniform, hygienically clean while
working in kitchen. Hands must be washed regularly at regular and appropriate times.
Ø
Nails
must be trimmed properly, no jewellery wearing even by female staff, and hairs
must be restrained by wearing chef cap or other restraints.
Ø
The
food should always be tasted with a spoon and this spoon should be reused only
after proper washing.
Ø
The
eating, drinking, consumption of tobacco should be restricted in a designated
area only where the contamination of food or food surface area may not take
place.
·
Transporting Food to remote sites
(satellite kitchens)
Ø
Frozen
food must always be kept frozen during transportation.
Ø
The
temperature of potentially hazardous foods must be maintained at 5oC
or below and cooked foods transported hot must be at 58oC. This
temperature must be maintained in food carrier as well.
Ø
The
food carrier must be cleaned thoroughly, washed, rinsed and sanitized properly.
The food carrier should have suitable containers with proper section to avoid
mixing of food during transportation, it should be leakage proof, easy to clean
and also approved for holding food.
·
Using Utensils while handling ready-to-eat foods
Ø
The
handling of ready-to-eat foods should never be bare handed except washing of
fruits and vegetables.
Ø
The
use of single-use gloves, deli tissue, foil wrap, tongs, ladles, spoons must be
incorporated while dealing with ready-to-eat foods.
Ø
The
hands should be washed properly after every task like before beginning a new
task, before beginning food preparation, after touching unclean utensils; and
after being interrupted such as answering phone calls, when being in operations
of cooking.
·
Limiting Bacterial growth in Potentially Hazardous Foods by Time
Ø
Establishing
written procedures and codes for identifying particular foods for which time
rather than temperature will be used to control bacterial growth, and procedures
followed when food is kept in danger zone for more than 4 hours.
Ø
The
raw potentially hazardous food should be cooked within 4 hours past the point
when the food is removed from temperature control.
Ø
Do
not mix the different batches of food together in the same container and in
case if they are mixed they should be cooked or served or discarded using the
time of the food in the first batch in the container.
·
Washing fruits and Vegetables
Ø
All
the raw fruits and vegetables should be thoroughly washed before combining it
with other ingredients. The washing of unpeeled fruits and vegetables to be
served must be done. The fresh produce must be washed under cold running water
or by permitted chemicals that comply with 2001 FDA Food Code.
Ø
The
fruits with firm surface must be scrubbed with brush meant for the same
purpose. The damaged or bruised areas must be removed, if any.
Ø
The
fresh-cut items must be labeled and marked with date and refrigerated.
Ø
The
service of raw seed sprouts should be avoided in preschool-age children.
·
Washing Hands
Ø
A
separate hand washing sink should be used for hand washing purpose. The sink
for food preparation, utility and dishwashing should not be used for hand
washing.
Ø
The
provision for warm running water, soap and means to dry the hand should be
provided.
Ø
The
hand should be washed at regular interval like before starting any task in food
area, during cooking, after using
toilets, sneezing, coughing etc.; after touching hairs, body or face, after
handling raw materials like meat, poultry etc.; after touching dirty dishes or
equipments, whenever anyone feels like his/her hands are contaminated and so
on.
Ø
The
hand should be washed using following procedures like washing hand and forearms
with running water at 38oC and with soap, hands should be scrubbed properly for
at least 15-20 seconds and then rinsed with water for 5-10 seconds.
Ø
Using
of hand sanitizer after hands are washed and dried properly.
All the
above mentioned guidelines must be complied with according to State or local
requirements that are based on the 2001
FDA Food Code.
Photographs used are from google 1.
Thank you readers!!





Nice sir
ReplyDeleteControlling time , temperature during preparation was very helpful. 🌹
ReplyDeleteIts very necessary for our daily life routine and thanks for elp us every time
ReplyDeleteRegard sahil wadhwa
👌Excellent Sir !
ReplyDeleteVery good sir... Excellent every onr should read it... ThoseTwhoTdont knowkabout food and food temperature good going👍👍👍👍✌️✌️✌️
ReplyDeleteYogesh,well done and most of the important points are covered by you in brief ...Kudos
ReplyDeleteGreat sir👍
ReplyDeleteReally informative and essential in our day to day life.
ReplyDeleteGreat work sir
ReplyDeleteReally informative and essential in our day to day life.
ReplyDeleteGreat one sir!!!
ReplyDeleteSir really informative and essential in our day to day life ..and one of the best article on HACCP
ReplyDeletenice work sir
ReplyDeletegood sir
ReplyDeleteperfect work👌👍👍👍
ReplyDeleteGreat one Sir.
ReplyDeleteGreat Sir
ReplyDelete